Age restrictions on video games are important content classification systems set by regulatory bodies like the ESRB (Entertainment Software Rating Board) and PEGI (Pan European Game Information). These systems protect younger audiences from inappropriate content and help parents make informed decisions when buying games. They provide warnings about violence, language, and mature themes before purchase, ensuring that players are aware of the content. Age restrictions also prevent underage access to extreme content, especially in countries with strict regulations.
These standardized frameworks evaluate multiple content descriptors, such as the intensity of violence, sexual content, language, substance use, and psychological elements within gaming experiences. As gaming platforms evolve from traditional consoles to mobile devices and virtual reality systems—the need for robust age-restriction frameworks becomes even more critical, addressing the impacts of new technologies on various age groups. In this article, AntGames will help you to understanding about video game age ratings, some core factors leading to this problem, and some useful tips for parents.
PEGI (Europe, UK, Middle East)
The Pan European Game Information (PEGI) system provides age classifications for interactive digital entertainment across Europe, the United Kingdom, and the Middle Eastern territories. This unified framework supports informed decision-making while allowing consumers to choose suitable gaming experiences.
PEGI uses five classification for video game age ratings:
- PEGI 3: Universal content, suitable for all ages. The game includes educational elements, positive themes, and minimal competitive interaction.
- PEGI 7: Features mild fantasy-based conflict, non-threatening situations, and content appropriate for children, with cartoon-like visuals.
- PEGI 12: Contains moderate simulated violence, mild language, and basic references to gambling in a controlled context.
- PEGI 16: Allows realistic depictions of violence, suggestive content, strong language, and mature themes appropriate for adolescent players.
- PEGI 18: For adult content, including graphic violence, explicit sexual material, substance abuse, and intense thematic elements.
The PEGI system includes content descriptors such as violence, language, fear, gambling, sex, drugs, discrimination, and in-game purchases. These ratings help parents, guardians, and consumers make informed decisions about which games are appropriate while respecting regional cultural values and ethical standards.
PEGI’s classification method aligns with other global systems like ESRB (North America) and CERO (Japan), ensuring consistency in-game content evaluation worldwide. This comprehensive system combines age-appropriate guidance with detailed content warnings, promoting responsible gaming practices for diverse audiences.

ESRB (North & Central America)
The Entertainment Software Rating Board (ESRB), established in 1994, is the official content classification system for video games in North America. It provides video game age ratings to help consumers make informed choices about digital entertainment. This system is used across North and Central America, offering standardized content evaluations to guide users in selecting age-appropriate games.
The ESRB rating system includes distinct categories:
- ‘E’ (Everyone): Suitable for all audiences.
- ‘E10+’: Content for players aged 10 and older, with more developed themes.
- ‘T’ (Teen): Suitable for players aged 13 and up, featuring moderate elements of intensity.
- ‘M’ (Mature): Restricted to individuals 17 and older, reflecting more intense content.
- ‘A’ (Adults Only): The most restrictive rating, for players aged 18 and above.
- ‘RP’ (Rating Pending): Given to products still awaiting evaluation during development.
The ESRB ensures transparency with detailed content descriptors and interactive elements, including warnings for digital interactions, in-game purchases, and user-generated content. The rating system also takes into account cultural differences across North and Central America while maintaining consistent evaluation standards.
This classification framework helps consumers, particularly parents, make well-informed decisions about video game content, ensuring a more enjoyable and appropriate gaming experience for all.

What Makes Games Get Age Ratings?
Age ratings are assigned based on a variety of content factors. These ratings help guide players, parents, and consumers in selecting appropriate games based on violence, language, themes, and cultural sensitivities.
Content Categories
Video game age ratings are based on several content categories that help guide consumers in choosing appropriate games. These evaluations assess various factors to determine a game’s suitability for different age groups.
Combat and conflict-related content plays a major role in age ratings, including the level of violence, graphic quality, and the consequences of actions within the game. Sexual themes are also considered, ranging from mild suggestive content to explicit material that can affect the rating. Language is another key factor, with profanity, maturity of dialogue, and cultural sensitivity influencing the overall classification. The portrayal of substances like alcohol, drugs, and tobacco is also factored in.
Regional rating systems reflect cultural norms. For instance, the Entertainment Software Rating Board (ESRB) in North America focuses primarily on violence, while the Pan-European Game Information (PEGI) system emphasizes gambling and discriminatory content. Psychological elements, like horror or emotional distress, also impact a game’s rating.
Cultural Considerations
Cultural differences play a major role in shaping video game classification systems and age ratings across global markets. These variations reflect unique socio-cultural values, regulatory frameworks, and local sensitivities. Each region evaluates gaming content through its own cultural lens, influenced by historical contexts and social norms. As a result, rating criteria and content restrictions vary from place to place.
Societal standards are crucial in content evaluation. Some regions may have a higher tolerance for combat or violent content, while others enforce stricter rules around intimate scenes, religious symbols, or political themes. These cultural factors have led to the development of localized rating systems that align with parental concerns, educational priorities, and community values.
Historical context also plays a significant role in classification decisions. Countries with sensitive historical experiences often apply more rigorous criteria for related content, ensuring that games are respectful of their cultural memory.

Parent’s Guide to Video Game Ratings
Content Evaluation Factors
Content evaluation factors in video game age ratings are essential for determining age-appropriate gaming experiences. The evaluation framework focuses on interactive gameplay mechanics, exploring player-environment interactions, skill development pathways, and cognitive engagement. Additionally, understanding the benefits of playing video games highlights how these interactive experiences can enhance problem-solving skills, improve hand-eye coordination, and foster social connections among players.
- Psychological Impact: This assessment considers the content’s intensity, emotional resilience requirements, and any potential effects on young players’ mental well-being.
- Social Interaction: Evaluates multiplayer dynamics, online community behaviors, and digital citizenship. Key elements include communication systems, player interaction frameworks, and online safety protocols.
- Educational Value: This factor looks at opportunities for cognitive development, such as computational thinking, creative problem-solving, and strategic reasoning.
- Narrative Analysis: Involves evaluating thematic elements, character arcs, and messaging. This includes examining plot structures, storytelling mechanisms, and value systems within the game.
- Rating Systems: Content is evaluated using standardized protocols, including ESRB (Entertainment Software Rating Board) and PEGI (Pan European Game Information) guidelines, along with regional classification frameworks, ensuring consistency across platforms and genres.
Important Considerations
Parents should understand that relying only on Entertainment Software Rating Board (ESRB) ratings and Pan European Game Information (PEGI) classifications doesn’t provide a full view of a game’s developmental suitability. While these ratings cover aspects like violence and mature themes, they don’t address factors like cognitive demands or social interaction.
For example, a game rated E (Everyone) or PEGI 3 may have challenges that are too complex for younger players, while T (Teen) or PEGI 12 titles can enhance cognitive skills like spatial awareness and decision-making.
Evaluating a game requires looking beyond ratings. Factors like gameplay complexity, time investment, and game features should be considered, as well as microtransactions and user-generated content that might expose children to unexpected scenarios.
Modern gaming platforms (PlayStation Network, Xbox Live, Steam, Epic Games, iOS, Android) offer parental controls that allow parents to manage screen time, communication, and spending limits.
By combining parental controls with careful content research, parents can ensure a safe and appropriate gaming experience for their children.
Tips for Parents
A comprehensive approach to selecting age-appropriate digital entertainment requires more than just relying on Entertainment Software Rating Board (ESRB) classifications and content descriptors. Parents should take the time to research thoroughly before purchasing games. This includes watching gameplay footage, reading reviews from professional gaming critics, and assessing how the game might impact children’s development in cognitive, behavioral, and educational areas.
Effective parental oversight involves active engagement throughout the gaming lifecycle. Initial family discussions should focus on the content, potential concerns, and children’s perspectives, encouraging open communication while ensuring that gaming choices align with family values.
After purchase, it’s essential to monitor children’s psychological development, social skills, and interactions during gameplay. Co-playing can turn gaming into a shared family experience, allowing parents to provide direct guidance and mentorship. Setting clear gaming rules, along with screen time guidelines, encourages a balanced lifestyle that includes physical activities, academic work, and socializing.
While content video game age ratings provide helpful initial guidance, they should not be considered absolute. Developmental stages, emotional resilience, and sensitivity to content can vary significantly among young players.

Recommended Browser Games Based on Age Rating
Looking for browser games that are both fun and suitable for different age groups? Whether you’re a parent helping your child choose games or a player seeking age-appropriate entertainment, this list has you covered. We’ve categorized games by age ratings, offering a range of options from family-friendly games to more intense, mature experiences. These games are safe, engaging, and easy to play directly in your browser, ensuring a great time for players of all ages.
For All Ages (E/PEGI 3 and CERO A)
Here’s a fun selection of browser games perfect for players of all ages, offering simple yet engaging gameplay with no complex content restrictions.
- Slither.io: A fun and addictive multiplayer game where you control a snake and eat food to grow longer while avoiding other snakes.
- Agar.io: This game involves controlling a cell that consumes smaller cells to grow larger, all while avoiding being eaten by bigger cells.
- Tetris: The classic puzzle game that challenges players to arrange falling blocks into complete lines. Simple, yet endlessly engaging, and suitable for all ages.
- Stick Fight: A multiplayer fighting game where players control stick figures in fast-paced combat. The cartoonish violence makes it suitable for older children and teens.

For Teens (T/PEGI 12 and CERO B)
Here are some exciting browser games for teens, offering fast-paced action, strategic gameplay, and competitive fun.
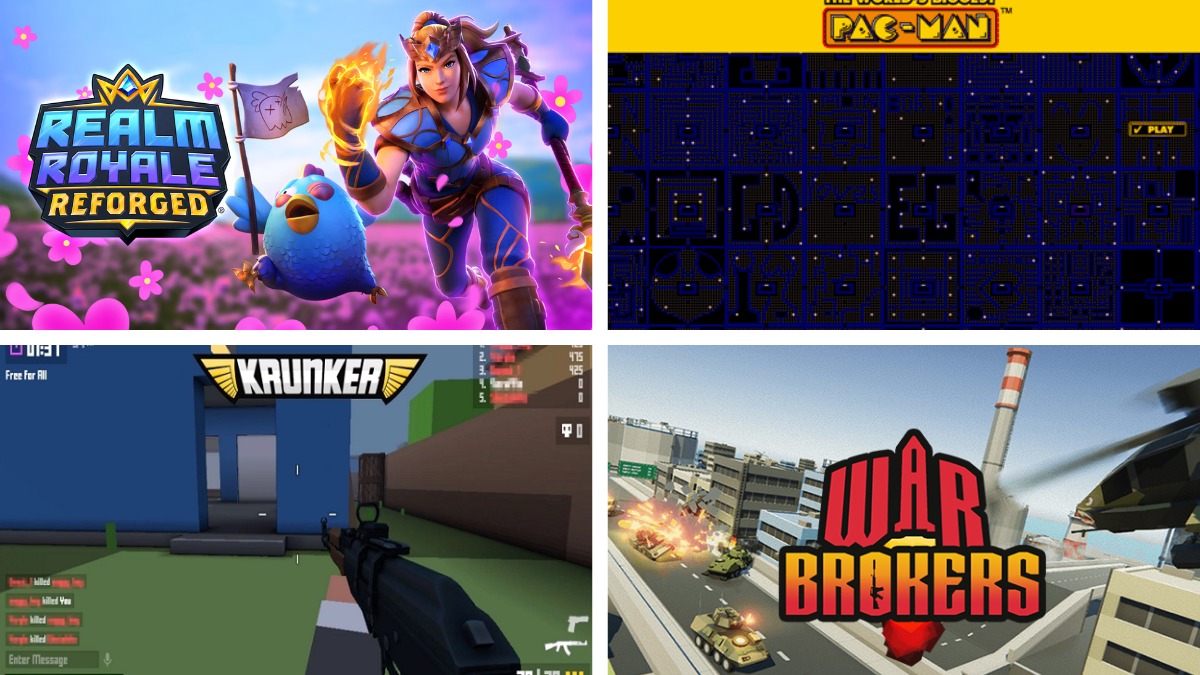
- Realm Royale: A battle royale game that mixes elements of traditional combat with unique character abilities.
- World’s Biggest Pac-Man: A modern, web-based take on the classic Pac-Man.
- Krunker.io: A fast-paced first-person shooter that you can play directly in your browser.
- War Brokers: A browser-based multiplayer first-person shooter game featuring fast action and various game modes.

For Mature Players (M/PEGI 18 and CERO Z)
These browser games for mature players offer intense action, strategic gameplay, and thrilling competition, perfect for those seeking a more challenging experience.
- HaxBall: A competitive, multiplayer sports game combining soccer and air hockey elements.
- Little Big Snake: A competitive browser game where you control a snake and consume other smaller snakes to grow larger.
- Tanki Online: An online multiplayer tank battle game with action-packed combat, involving explosions and tactical gameplay.

For Everyone (E10+/PEGI 7 and CERO A/B)
These browser games offer exciting and accessible experiences for everyone, with a mix of strategy, creativity, and fun multiplayer action.
- Skribbl.io: A fun, multiplayer drawing and guessing game. Players take turns drawing an image based on a given word while others try to guess it.
- Tower Defense Games: A genre of games where players must defend their towers from incoming waves of enemies by placing different types of defense units along the path
- Zombs Royale: A battle royale game played in a 2D top-down view. Players fight to be the last one standing while looting weapons and avoiding other players.

Which is a Trustworthy Website for Playing Video Games?
If you’re looking for a reliable platform to play video games, AntGames is a top choice. AntGames offers a wide variety of free, browser-based games across multiple genres, catering to all types of players. Whether you’re into action games, arcade games, driving games, shooting games or skill games, AntGames has something for everyone. The site provides a secure, safe environment with no hidden fees or harmful content. Plus, you can jump right into the action—no downloads or complicated installations needed. AntGames ensures a fun, family-friendly experience for players of all ages.
What’s the difference between PEGI and ESRB?
PEGI (Pan European Game Information) and ESRB (Entertainment Software Rating Board) are two video game content rating systems serving Europe and North America. Both aim to protect young players and assist consumers in choosing age-appropriate games, including Browser Games, which are easily accessible online and often played by a wide range of age groups.
- PEGI uses a numerical age classification system (3, 7, 12, 16, 18) along with content descriptors like violence, fear, discrimination, drugs, gambling, and sexual content. This system is particularly strict regarding violence, especially in games with realistic combat mechanics.
- ESRB uses categories such as Early Childhood (EC), Everyone (E), Everyone 10+ (E10+), Teen (T), Mature (M), and Adults Only (AO), with detailed content analysis.
Both systems help consumers identify age-appropriate content and serve as authoritative content classification standards within the global gaming industry.
See more: List of video game genres
Why are games 17+ instead of 18+?
Games are rated 17+ rather than 18+ because the ESRB (Entertainment Software Rating Board) believes 17-year-olds, typically high school seniors, have the cognitive and emotional maturity to handle mature content. The 17+ rating reflects the cultural norm where 17 marks the transition from adolescence to adulthood, giving individuals more autonomy. This rating allows developers to include mature themes, violence, and strong language while appealing to late adolescents, striking a balance between artistic expression and content regulation.
Are Ratings Legally Enforced?
Video game age ratings are enforced differently across regions. In North America, ESRB ratings are voluntary guidelines, and retailers choose whether to enforce them. There is no federal law requiring compliance when selling mature games to minors.
However, in many international markets, ratings are legally enforced. The PEGI system has legal authority in the EU, while Germany’s USK ratings are binding, with penalties for non-compliance. Japan’s CERO and Australia’s Classification Board also have legally enforced rating systems.
Age restrictions in video games are essential for protecting young players from inappropriate content. Rating systems like ESRB, PEGI, and CERO evaluate factors such as violence, explicit language, and mature themes to assign age classifications. These ratings help parents and guardians make informed decisions about what games are suitable for their children across platforms like consoles, PC, mobile, and virtual reality. By following these guidelines, the gaming community ensures safe and age-appropriate experiences for all players. Play responsibly and choose age-appropriate games for a safe gaming environment.
If your children desire to experience a safe gaming platform containing a wide range of fantastic games, you can visit AntGames to explore fun online games to play with friends to suggest for your kids.





